How Bleaching Earth Contributes to the Purification of Edible Oils
| Key Takeaway | Details |
|---|---|
| Role of Bleaching Earth | Essential for removing impurities and improving the appearance of oils. |
| Types of Bleaching Earth | Two main types: natural (basic filtration) and activated (enhanced adsorption). |
| Oil Decolorization | Removes pigments, making oils clearer and more suitable for consumption. |
| Impact on Oil Quality | Enhances purity, clarity, shelf life, and ensures oils meet food safety standards. |
| Industrial Applications | Used in edible oil production, cosmetics, and biodiesel. |
Table of Content
Introduction: The Role of Bleaching Earth in Oil Purification
Bleaching earth plays a crucial role in purifying edible oils, making them safe and appealing for consumers worldwide. It is an essential part of edible oil refining, responsible for removing impurities and enhancing the appearance of oils. Through its natural adsorption properties, bleaching earth acts as a powerful filtration agent, ensuring that oils used in cooking and food production meet the highest standards of quality and safety.
Industries Benefiting from Bleaching Earth
| Industry | Use of Bleaching Earth |
|---|---|
| Edible Oil Production | Removes color and impurities from oils |
| Cosmetics | Used in refining oils for cosmetic formulations |
| Biodiesel Production | Removes contaminants from biodiesel feedstocks |
The importance of oil purification cannot be overstated, especially in industries where the appearance and quality of the oil directly impact product safety and marketability. Bleaching earth is an integral part of this process, ensuring oils are free from unwanted contaminants and ready for consumption.
What is Bleaching Earth?
At its core, bleaching earth is a highly adsorbent clay used to remove impurities from oils. It typically consists of bentonite clay, which has natural adsorptive properties, and activated clay, which undergoes treatment to enhance its efficiency in capturing contaminants. This makes bleaching earth indispensable in the oil purification process.
Activated clay is especially effective in industrial oil purification, removing contaminants like pigments, metals, and other unwanted particles that affect the color and quality of oils. Whether natural or activated, bleaching earth is critical in ensuring oils are visually appealing and safe for consumption.

How Does Bleaching Earth Work in the Oil Filtration Process?
The power of bleaching earth lies in its unique ability to capture impurities, a process crucial to edible oil refining. The key mechanism behind this is adsorption, where the clay’s highly porous structure allows it to attract and bind unwanted particles such as pigments, trace metals, and oxidation by-products. When heated oil flows through the bleaching earth, these contaminants are trapped on its surface, leaving behind a cleaner, more purified oil. This action is particularly vital in oil decolorization, as it helps remove pigments that affect both the appearance and stability of the final product.
Common Impurities Removed by Bleaching Earth
| Impurity | Effect on Oil | Removed by |
|---|---|---|
| Pigments (e.g., carotenoids) | Causes unwanted color in oils | Adsorption onto bleaching earth |
| Trace Metals (e.g., iron) | Promotes oxidation, reduces shelf life | Adsorption via activated clay |
| Phospholipids | Affects stability, causes cloudiness | Adsorbed during bleaching process |
The decolorization process is not just cosmetic—it also improves the oil’s overall quality and shelf life. Without this step, oils would remain darker and carry undesirable tastes or odors, making them less suitable for consumption or further processing. By using bleaching earth in this phase of oil purification, producers can ensure that the oil meets strict industry standards for clarity, taste, and safety, making it ideal for food production and other industrial uses.
The Bleaching Process
The bleaching process itself is a multi-stage operation that begins with preparation, where the raw oil is first heated to reduce its viscosity, allowing for better interaction with the bleaching earth. The amount and type of bleaching earth used in this stage depend on the oil’s initial quality and the desired level of purification. Factors like the oil’s acidity, color, and impurity level dictate whether natural bentonite clay or activated clay will be more effective in achieving optimal results.
Once the oil and bleaching earth are combined, the adsorption stage begins. As the oil is stirred, the impurities—including unwanted colors, oxidation products, and trace metals—adhere to the surface of the bleaching earth particles. This process is what makes the oil clearer and safer for consumption. The mixture is then subjected to the separation phase, where the oil is filtered or centrifuged to remove the spent bleaching earth, now known as exhausted sorbent. This waste is carefully managed, as it contains the captured impurities. The refined oil moves on to further refining stages, such as winterization (for oils that need to remain liquid at low temperatures) and deodorization, where any remaining odors are removed, often using steam.
The end result of the bleaching process is a highly purified, decolorized oil that is free from impurities and suitable for a wide range of applications, from cooking to industrial use.
- Preparation: The oil is heated and mixed with an appropriate amount of bleaching earth. The choice of bleaching earth depends on factors such as the type of oil and the desired level of purification.
- Adsorption: As the oil and bleaching earth mixture is stirred, the impurities in the oil are adsorbed onto the surface of the bleaching earth particles. This process is also known as oil decolorization.
- Separation: Once the adsorption process is complete, the oil is separated from the bleaching earth using filtration or centrifugation methods. The spent bleaching earth, now called exhausted sorbent, is removed as waste.
- Further refining: The oil may undergo further refining steps, such as winterization (for specific oils) and deodorization, to achieve the desired quality.
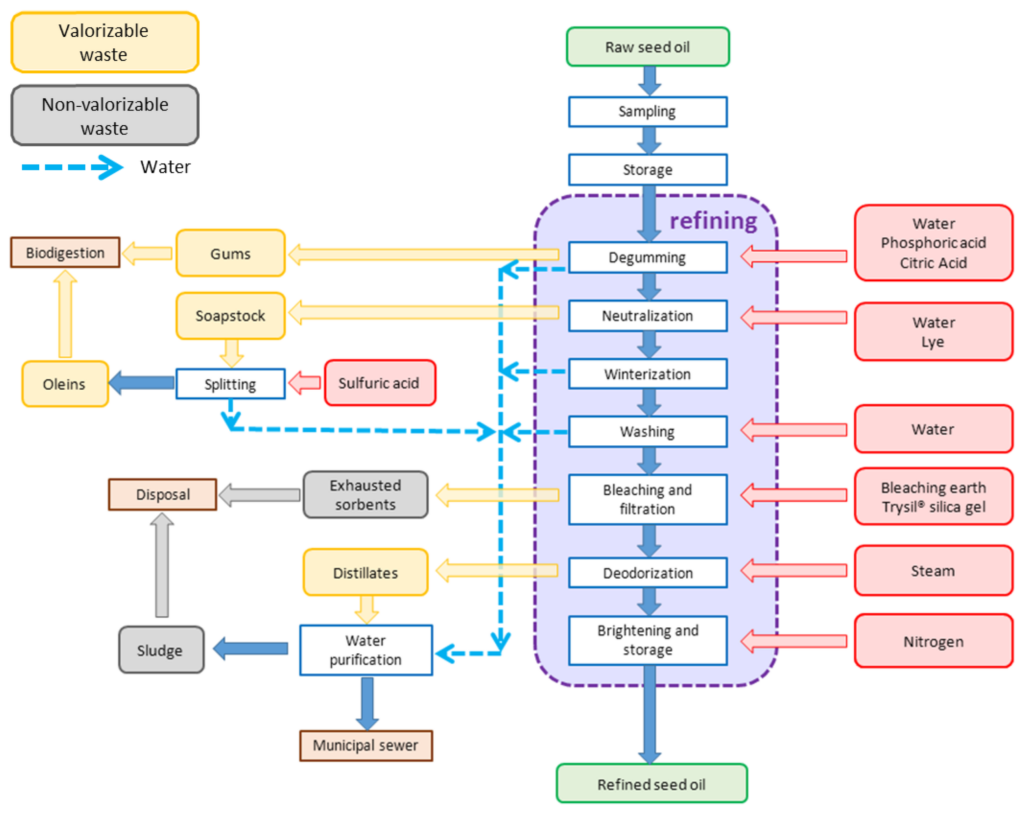
Stages of the Bleaching Process
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Preparation | Oil is heated, and bleaching earth is added to the mixture |
| Adsorption | Impurities bind to the surface of the bleaching earth |
| Separation | Oil is filtered to remove exhausted bleaching earth |
| Further Refining | Steps like deodorization or winterization occur post-bleaching |
Types of Bleaching Earth: Natural vs. Activated
Bleaching earth comes in two main types: natural and activated, each with unique properties suited to different industrial applications.
Natural bleaching earth, typically bentonite clay, is minimally processed and used for basic filtration, offering satisfactory adsorption capabilities for standard purification tasks. This type of clay is especially useful when the oil does not require extensive purification and when cost-efficiency is prioritized.
However, for more demanding applications, such as edible oil refining where higher purity standards are critical, activated bleaching earth is the preferred option. Activated bleaching earth undergoes a chemical treatment process—typically acid activation—that enhances its adsorption capacity. This process involves treating the clay with acid to increase the number of active sites on its surface, which significantly improves its ability to trap and remove impurities such as pigments, metals, phosphatides, and oxidation products.
The enhanced efficiency of activated bleaching earth makes it ideal for oil decolorization in the edible oil industry, where the clarity, color, and overall quality of the oil are critical. For example, activated clay is frequently used in the refining of vegetable oils like soybean, palm, and sunflower oils, where removing contaminants ensures that the oil meets health and safety standards for consumption. The decision to use natural or activated bleaching earth depends on the level of purification required, cost considerations, and the specific properties of the oil being processed.
Comparing Natural and Activated Bleaching Earth
| Property | Natural Bleaching Earth (Fuller’s Earth) | Activated Bleaching Earth |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Earth’s crust | Treated natural bleaching earth |
| Composition | Aluminum silicates, trace minerals | Acid-activated aluminum silicates |
| Adsorption capacity | Moderate | High |
| Applications | Edible oil refining, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals | Edible oil refining, industrial applications |
Exhausted Sorbent: Waste Management
The exhausted sorbent, or spent bleaching earth, is a waste product generated during the edible oil purification process. Proper disposal or recycling of this waste material is essential to minimize its environmental impact. Some common methods for managing exhausted sorbent include landfilling, incineration, and recycling for use in animal feed, fertilizer, or other industrial applications.
Why Bleaching Earth is Vital in Edible Oil Refining
Bleaching earth plays a crucial role in ensuring that edible oils are both visually appealing and safe for consumption. In the refining process, oils contain various impurities such as metals, pigments, and oxidation products, which can negatively impact their color, clarity, and overall quality. Bleaching earth effectively removes these impurities through adsorption, ensuring that the oils meet industry standards for purity and safety.
Additionally, the removal of these contaminants not only enhances the oil’s aesthetic appeal but also significantly improves its shelf life. Impurities like free fatty acids, phospholipids, and trace metals can cause the oil to degrade over time, leading to off-flavors, rancidity, and reduced stability. By eliminating these harmful substances, bleaching earth helps maintain the freshness and stability of the oil, ensuring it remains fit for consumption for longer periods.
Furthermore, in the food production industry, the color of the oil is often a key quality marker. Consumers expect oils to be clear and golden or light in appearance, depending on the type of oil. Bleaching earth is critical in achieving this desired oil decolorization, making the product more appealing to both consumers and manufacturers. This ensures that edible oils, whether they are used in cooking, frying, or processed food production, meet the stringent aesthetic and safety expectations of the industry.
The Benefits of Using Bleaching Earth in Oil Purification
Beyond simply removing contaminants, bleaching earth offers a range of benefits that impact both oil producers and consumers. Its ability to efficiently decolorize and purify oils ensures that the end product meets industry standards while maintaining cost-effectiveness. The use of bleaching earth in oil clarification not only improves the oil’s appearance but also ensures that it is free from harmful substances.
Benefits of Using Bleaching Earth in Edible Oil Refining
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Improved Clarity | Removes color and cloudiness from oils |
| Extended Shelf Life | Adsorbs oxidation-promoting impurities, enhancing stability |
| Safety and Compliance | Ensures oils meet food industry quality and safety standards |
In addition, bleaching earth is highly efficient in oil bleaching and provides manufacturers with a reliable solution to maintaining the purity and stability of their oils, contributing to a higher-quality product overall.
Challenges in Using Bleaching Earth and How to Address Them
While bleaching earth is highly effective, using it in oil purification can present some challenges. One of the most common issues is selecting the right type of bleaching earth for different oils. Certain oils require natural clay, while others benefit more from the use of activated clay. Selecting the appropriate type ensures optimal filtration and purification results.
Factors Affecting Bleaching Earth Performance
| Factor | Impact on Efficiency | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Temperature | Affects adsorption rate | Preheat oil to optimal temperature for filtration |
| Type of Bleaching Earth | Determines adsorption capacity | Select natural or activated clay based on oil requirements |
| Dosage | Insufficient dosage reduces impurity removal | Test and adjust dosage for maximum purification |
Another challenge is managing the waste generated from spent bleaching earth after the filtration process. To address this, industries can implement waste management solutions, such as recycling the spent clay or safely disposing of it according to environmental regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can bleaching earth be reused?
Bleaching earth can be regenerated and reused to some extent. However, its effectiveness in adsorbing impurities and decolorizing oil diminishes with each use. After a certain point, it is no longer economical to reuse bleaching earth and must be replaced.
How do you activate bleaching earth?
Bleaching earth is activated through a process that typically involves heating the clay at high temperatures, followed by treatment with acid or other chemicals. This process increases the clay’s adsorption capacity and enhances its decolorization properties.
How do you dispose of bleaching earth?
Spent bleaching earth should be disposed of according to local environmental regulations. It may be used as an additive in composting or landfills, or incinerated in some cases.
How do you use bleaching earth for pyrolysis oil?
Bleaching earth can be used in the purification of pyrolysis oil by mixing it with the oil at the appropriate dosage. The mixture is then agitated, allowing the bleaching earth to adsorb impurities and decolorize the oil. Finally, the spent bleaching earth is separated from the oil, leaving behind a cleaner product.
Is bleaching earth flammable?
Bleaching earth is not considered flammable. However, spent bleaching earth may contain residual oil, which could pose a fire risk if not properly handled or stored.
Is bleaching earth hazardous?
Bleaching earth itself is generally not hazardous. However, spent bleaching earth may contain residual oil and chemicals, which can be harmful to the environment and pose health risks if not managed properly.
Is bleaching earth or clay?
Bleaching earth is a type of clay, specifically, a naturally occurring material composed of various minerals, primarily montmorillonite, and other smectite-group minerals.
What are examples of bleaching earth?
Examples of bleaching earth include Fuller’s Earth, activated bleaching clay, and activated bleaching earth.
What does bleaching earth mean?
Bleaching earth refers to a clay material used in the purification and decolorization of edible oils and other substances. It has a strong adsorption capacity and can remove impurities, such as pigments, phospholipids, and oxidation products, from oil.
What is activated bleaching earth used for?
Activated bleaching earth is primarily used in the purification and decolorization of edible oils, fats, and waxes. It is also employed in the removal of impurities from industrial oils and other chemical processes.
What is another name for bleaching earth?
Another name for bleaching earth is Fuller’s Earth.
What is bleaching earth made of?
Bleaching earth is made of various minerals, primarily montmorillonite, and other smectite-group minerals, which give it its adsorption and decolorization properties.
What is good earth bleaching earth?
“Good Earth” bleaching earth typically refers to a high-quality bleaching earth product that effectively removes impurities and decolorizes oils and fats.
What is spent earth oil?
Spent earth oil refers to the residual oil and impurities adsorbed by bleaching earth after it has been used in the purification process.
What is the chemical name for bleaching earth?
The chemical name for bleaching earth is typically activated bentonite clay or activated fuller’s earth. It primarily consists of montmorillonite, a clay mineral that has undergone acid activation to enhance its adsorption capacity. This treatment increases its effectiveness in removing impurities, pigments, and contaminants from oils and other substances during the refining process.
What is the pH of bleaching earth?
The pH of bleaching earth can vary depending on the specific product and its composition. Generally, it ranges from neutral to slightly acidic, with a pH value between 6 and 8. However, some activated bleaching earth products may have a lower pH due to the acid activation process.
Conclusion: The Future of Bleaching Earth in Oil Purification
As oil refining processes continue to evolve, the role of bleaching earth will remain integral to ensuring quality and safety in edible oils. Whether used in industrial oil purification or in the food production process, bleaching earth will continue to be a critical component in maintaining the quality of oils consumed worldwide.
With advancements in activated clay technology and a growing emphasis on oil purification, bleaching earth is set to play an even more important role in refining processes. As consumer demand for cleaner, higher-quality oils increases, the future of bleaching earth looks promising.
For more information about bleaching earth, you can explore our Bleaching Earth products. Additionally, refer to our Complete Guide to Bleaching Earth for more detailed insights, and read our previous post, The Magic of Bleaching Earth: A Complete Guide 2024. Check out our premium Activated Clay Bleaching Earth for high-performance oil purification.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only. Always consult industry professionals for specific guidance on using bleaching earth in your processes.
Read more
The Magic of Bleaching Earth: A Complete Guide 2023
How Bleaching Earth Contributes to the Purification of Edible Oils
ประโยชน์ของดินฟอกสีสำหรับกรองน้ำมัน
เร่งดินเหนียวฟอกสีใช้ทำน้ำมันอาหารได้อย่างปลอดภัยและมีประสิทธิภาพ
ดินเหนียวฟอกสี Bleaching Earth
