Molecular Sieves Types and Applications
| Key Takeaway | Details |
|---|---|
| What are Molecular Sieves? | Highly porous materials used for adsorbing gases and liquids based on molecular size. |
| Types of Molecular Sieves | Includes 3A, 4A, 5A, and 13X types, each suited for different applications based on pore size. |
| Key Applications | Used in gas drying, air separation, oxygen generation, and petrochemical industries. |
| Role in Oxygen Generation | Molecular sieves like 13X are critical in Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA) systems for producing medical-grade oxygen. |
| Advantages | High adsorption efficiency, selectivity for certain molecules, and reusability after regeneration. |
| Choosing the Right Molecular Sieve | Depends on factors like pore size, gas composition, and required purity levels. |
Table of Contents
Molecular sieves types and applications
Molecular sieves play a vital role in various industries thanks to their unique properties. In this article, we will explore the different types of molecular sieves, their applications, and benefits. Let’s dive in!
What are Molecular Sieves?
Molecular sieves are crystalline, porous materials known for their exceptional ability to separate and purify gases and liquids. They are often made from natural or synthetic zeolites and exhibit unique adsorption properties.
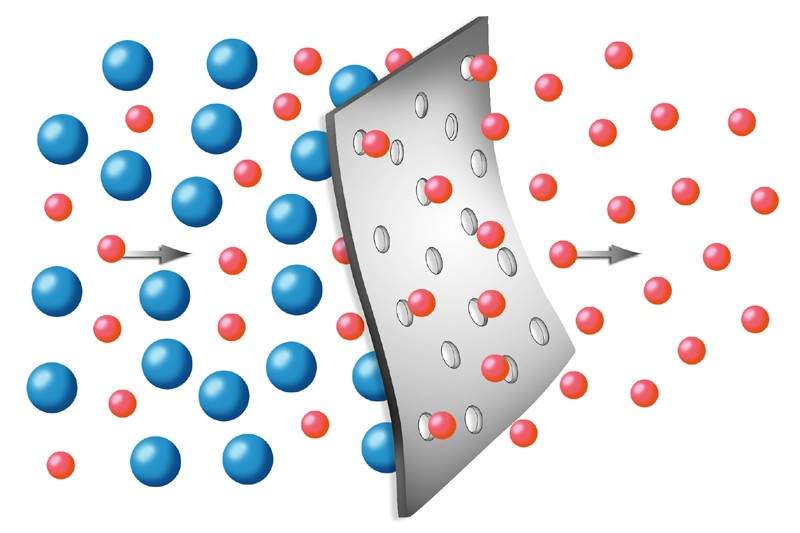
Natural molecular sieves are minerals that occur in nature, whereas synthetic molecular sieves are manufactured in a controlled environment. The structure and composition of molecular sieves are characterized by their interconnected channels and cavities, which allow for selective adsorption of molecules based on their size and shape.
Common Impurities Removed by Molecular Sieves in Key Applications
| Impurity | Removed by | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Water Vapor | 3A, 4A, 13X | Solvent drying, natural gas purification, air drying |
| Carbon Dioxide | 4A, 13X | Air separation, gas purification |
| Hydrocarbons | 5A | Petrochemical industry, natural gas processing |
| Nitrogen | MSOX-500, MSOX-501 | Oxygen generation in PSA systems |
Types of Molecular Sieves
There are several common types of molecular sieves, including 3A, 4A, 5A, and 13X. Each type has a specific pore size and adsorption capacity, allowing them to excel in different applications.
3A Molecular Sieve
Overview
Explore our 3A Molecular Sieve Product
With a pore size of approximately 3 angstroms, 3A molecular sieves are often used for drying gases and liquids, as well as the removal of small molecules like water.
Pore Size
- ~3 angstroms
Main Application
3A molecular sieves are primarily used for drying gases and liquids by removing moisture. Their small pore size allows them to adsorb water molecules while excluding larger molecules like hydrocarbons. This makes them ideal for applications where moisture needs to be removed without affecting other compounds.
Specific Use Cases
- Dehydration of ethanol in the production of high-purity ethanol.
- Drying natural gas and other gases like hydrogen and argon.
- Preventing moisture contamination in pharmaceutical and electronic packaging.
4A Molecular Sieve
Overview
Explore our 4A Molecular Sieve Product
With a larger pore size of around 4 angstroms, 4A molecular sieves can adsorb molecules like water, ammonia, and carbon dioxide.
Pore Size
- ~4 angstroms
Main Application
The 4A molecular sieve has a slightly larger pore size than the 3A type, allowing it to adsorb not only water but also molecules like ammonia and carbon dioxide. It is widely used for both drying and purifying gases and liquids.
Specific Use Cases
- Air separation: Removing moisture and carbon dioxide from air to purify it before liquefaction or separation.
- Dehydration of refrigerants to prevent freezing in refrigeration systems.
- Drying solvents such as methanol, ethanol, and other polar compounds in the chemical industry.
5A Molecular Sieve
Overview
Explore our 5A Molecular Sieve Product
Featuring a pore size of approximately 5 angstroms, 5A molecular sieves can separate normal paraffins from isoparaffins and other hydrocarbons.
Pore Size
- ~5 angstroms
Main Application
The 5A molecular sieve is designed with a pore size large enough to adsorb normal paraffins (straight-chain hydrocarbons) while excluding isoparaffins (branched hydrocarbons). This makes it ideal for separation and purification processes in the petrochemical industry.
Specific Use Cases
- Separation of n-paraffins from isoparaffins in hydrocarbon streams for fuel and chemical manufacturing.
- Hydrogen purification in refinery processes.
- Natural gas drying and purification by removing contaminants like carbon dioxide and water vapor.
13X Molecular Sieve
Overview
Explore our 13X Molecular Sieve Product
With the largest pore size of about 10 angstroms, 13X molecular sieves are particularly effective in air separation and the removal of larger molecules.
Pore Size
- ~10 angstroms (largest pore size among the common molecular sieves)
Main Application
The 13X molecular sieve has the largest pore size, allowing it to adsorb much larger molecules compared to 3A, 4A, and 5A sieves. It is especially effective in air separation and purification processes for removing carbon dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, and larger contaminants from gases. See also: The Versatility of 13x Molecular Sieves and Their Unique Application
Specific Use Cases
- Oxygen generation: Used in Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA) systems for separating oxygen from nitrogen.
- Air purification: Removes moisture, carbon dioxide, and other contaminants from air before liquefaction.
- Industrial gas purification: Widely used for removing large impurities from gas streams, such as in natural gas processing and petrochemical production.
MSOX-500 and MSOX-501
Overview
Explore our MSOX Molecular Sieve Products
MSOX-500 and MSOX-501 are specialized molecular sieves primarily used in Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA) oxygen generators for producing high-purity oxygen. These sieves are designed to efficiently separate nitrogen from oxygen, making them ideal for both industrial and medical oxygen concentrators.
MSOX-500
MSOX-500 is tailored for use in larger industrial oxygen generation systems, such as those employed in wastewater treatment and aquaculture, where higher volumes of oxygen are required. It can achieve oxygen purity levels of up to 93% ± 3%.
MSOX-501
MSOX-501 is specifically developed for portable oxygen concentrators used in medical applications. It is commonly used in devices with a flow rate of 1-5 liters per minute. The key advantage of MSOX-501 is its ability to generate high-purity oxygen in smaller, more compact systems, making it highly suitable for home oxygen concentrators and medical environments.
Features
Both molecular sieves feature excellent nitrogen adsorption capacity and nitrogen/oxygen separation efficiency, contributing to faster oxygen production rates and longer operational lifespans, making them highly effective in various PSA applications. See also: The Power of MSOX Molecular Sieves
Specific Advantages
These molecular sieves are seen as an advanced alternative to traditional 5A (CaA) molecular sieves, providing higher performance in terms of both adsorption and oxygen production.
Types of Molecular Sieves and Their Applications
| Molecular Sieve Type | Pore Size | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| 3A | 3 angstroms | Drying polar liquids, moisture control in packaging, solvent drying |
| 4A | 4 angstroms | Air and gas purification, drying of refrigerants, ammonia, and carbon dioxide adsorption |
| 5A | 5 angstroms | Hydrocarbon separation, natural gas drying, hydrogen purification |
| MSOX-500 | 5 angstroms | High-purity oxygen production for industrial and medical oxygen generators |
| MSOX-501 | 5 angstroms | Portable oxygen generation, suitable for mobile and smaller-scale applications |
| 13X | 10 angstroms | Air separation, oxygen production, industrial gas purification, CO2 removal |
The key component in molecular sieves is zeolite, a naturally occurring mineral with a unique, microporous structure that enables it to selectively adsorb molecules.

Key Applications of Molecular Sieves
Molecular sieves find use in a wide range of industries and applications due to their versatile properties. Here are some of the most common applications:
A. Petrochemical Industry
- Gas Purification and Separation:
Molecular sieves like 5A are commonly used in the petrochemical industry for separating and purifying gases. The 5A sieve, with its pore size of approximately 5 angstroms, can effectively adsorb normal paraffins from mixtures of hydrocarbons, helping separate specific gas components. It is particularly useful in processes such as hydrogen purification and the removal of impurities like carbon dioxide and moisture from gas streams. - Drying of Solvents and Feedstocks:
Both 3A and 4A molecular sieves are effective in drying solvents and petrochemical feedstocks. The 3A molecular sieve is typically used when the solvent contains unsaturated hydrocarbons, as its small pore size excludes these larger molecules, ensuring only water is adsorbed. For more general solvent drying where larger molecules are not a concern, the 4A molecular sieve can adsorb water, ammonia, and carbon dioxide, ensuring the feedstocks are free from moisture, which could otherwise disrupt downstream chemical processes.
B. Pharmaceutical Industry
- Solvent Drying:
In pharmaceutical production, maintaining high purity levels of solvents is critical. 3A molecular sieves are ideal for drying polar solvents used in pharmaceutical applications. They can adsorb water molecules without interacting with the active ingredients or solvents being used, ensuring the integrity of the drug manufacturing process. 4A molecular sieves are also used in drying non-polar solvents to maintain the required purity standards in pharmaceutical manufacturing. - Protection of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs):
Moisture is a major threat to the stability and effectiveness of APIs. 3A and 4A molecular sieves are commonly employed to maintain low humidity levels in pharmaceutical packaging or during storage. The ability of these sieves to precisely control moisture levels ensures that APIs remain stable and effective for extended periods, preventing degradation that could compromise the efficacy of the drug.
C. Food and Beverage Industry
- Moisture Control and Preservation:
3A molecular sieves are frequently used in the food and beverage industry to control moisture levels in packaging. Their selective adsorption of water prevents spoilage caused by excess moisture, maintaining the quality of the food product. The 3A pore size is ideal for food packaging applications as it excludes larger molecules that could affect the product’s composition while only targeting water vapor. - Oxygen Scavenging in Packaging:
13X molecular sieves are highly effective in oxygen removal from food packaging. By adsorbing both oxygen and water vapor, these sieves can prevent oxidation and spoilage of food products. This helps extend the shelf life of perishable goods such as snacks, baked goods, and processed foods by keeping the environment inside the packaging oxygen-free.
D. Air Separation and Compression
- Nitrogen and Oxygen Generation: 13X molecular sieves play a critical role in Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA) systems, which are used for producing high-purity nitrogen or oxygen from atmospheric air. The 13X sieve has a large pore size, making it capable of adsorbing nitrogen while allowing oxygen to pass through, which is essential in medical and industrial oxygen generation processes.
The MSOX-500 and MSOX-501 molecular sieves are advanced types of X-type sieves, optimized specifically for oxygen generation.- MSOX-500 is designed for industrial oxygen concentrators, such as those used in wastewater treatment and aquaculture.
- MSOX-501 is used in portable oxygen concentrators for medical applications, delivering 1-5 liters per minute of oxygen for patients requiring respiratory support. Both sieves ensure oxygen purity levels of up to 93% ± 3%, making them crucial in healthcare and industrial settings.
- Removal of Impurities in Air Systems: In compressed air systems, 4A and 13X molecular sieves are commonly used to remove moisture, carbon dioxide, and other impurities that could damage equipment or reduce air quality. By using these sieves, industries can ensure clean, dry air for applications ranging from pneumatic systems to refrigeration units.
Steps in the Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA) Process
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Adsorption | Nitrogen is adsorbed by the molecular sieve (e.g., 13X, MSOX-500, MSOX-501), leaving pure oxygen. |
| Pressure Release | The pressure is reduced, allowing the sieve to release the adsorbed nitrogen. |
| Regeneration | The molecular sieve is regenerated by venting or purging with oxygen or another gas. |
| Purification | The final oxygen product is collected for industrial or medical use. |
E. Environmental Applications
- Removal of Pollutants in Water and Air: 5A and 13X molecular sieves are widely used in environmental protection efforts for purifying both water and air. In water treatment, molecular sieves can adsorb harmful contaminants such as heavy metals and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). In air purification systems, 13X sieves remove pollutants such as carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and nitrogen oxides from industrial emissions, contributing to cleaner air.
- Carbon Capture and Storage: 13X molecular sieves are increasingly being employed in carbon capture technologies aimed at reducing carbon dioxide emissions. By efficiently adsorbing CO2 from flue gases in industrial processes, 13X sieves help mitigate climate change by facilitating the storage or utilization of captured carbon dioxide. This makes them an essential tool in efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat global warming.
F. Natural Gas Purification
- Molecular sieves like 5A and 13X are widely used in the natural gas industry to purify gas streams by removing contaminants such as water vapor, carbon dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, and even heavy hydrocarbons. These impurities can cause corrosion in pipelines and reduce the efficiency of natural gas processing equipment. Molecular sieves ensure that natural gas meets the necessary purity levels for safe transport and use.
G. Refrigeration and Air Conditioning
- 4A molecular sieves are used in refrigeration and air conditioning systems to remove moisture and prevent freezing or corrosion in refrigerants. They help keep the systems running efficiently by preventing water-induced freezing and ensuring that refrigerants remain free from moisture, which could otherwise lead to performance issues or equipment damage.
H. Chemical Processing
- In chemical processing, molecular sieves are crucial in catalysis and separation processes. For example, 5A molecular sieves are used in the isomerization of hydrocarbons to selectively separate straight-chain hydrocarbons from branched ones, a key step in producing high-octane fuels. Molecular sieves also serve as catalysts or catalyst carriers in many chemical reactions, improving the efficiency and selectivity of these processes.
I. Oil Refining
- In addition to edible oils, molecular sieves are used in petroleum refining for the purification of crude oil and other hydrocarbons. 5A molecular sieves can be used to separate normal paraffins from isoparaffins, which is essential for producing cleaner, higher-quality fuels. This process ensures that the final product meets fuel standards and regulations.
J. Hydrogen Purification
- 5A molecular sieves are used in hydrogen production to purify hydrogen gas by removing contaminants such as water, carbon dioxide, and hydrocarbons. Hydrogen is widely used in fuel cells, refining processes, and ammonia production, and it needs to be extremely pure for these applications. Molecular sieves help achieve the required purity levels.
K. Biofuels and Renewable Energy
In the biofuel industry, achieving high-purity fuel-grade ethanol is crucial for optimal engine performance and emission control. Molecular sieves, especially 3A sieves, play an essential role in ethanol dehydration by selectively removing water from the ethanol mixture. This process is vital for producing anhydrous ethanol, which meets the stringent purity standards required for fuel applications in renewable energy. See Molecular Sieves for Ethanol Dehydration: Ensuring Purity and Efficiency
By facilitating efficient ethanol production, molecular sieves support sustainable energy goals and are integral to biofuel production processes. For more on how molecular sieves are employed across industries, see Molecular Sieves Types and Applications.
Benefits of Using Molecular Sieves
Molecular sieves offer numerous benefits in various industries, some of which include:
1. High Adsorption Capacity
Molecular sieves can adsorb large quantities of molecules, making them highly effective for purification and separation processes. This high capacity allows for improved process efficiency and reduced costs in many applications.
2. Selectivity
The unique pore structure of molecular sieves allows for the selective adsorption of specific molecules based on their size and shape. This selectivity ensures high levels of purity in the separated components and is especially valuable in industries where precision is crucial.
3. Regenerability
Molecular sieves can be regenerated and reused multiple times, making them an environmentally friendly and cost-effective solution. By applying heat or a vacuum, the adsorbed molecules can be removed, allowing the molecular sieve to regain its adsorption capacity.
4. Stability and Durability
Molecular sieves are chemically and thermally stable, which means they can withstand harsh operating conditions and maintain their adsorption properties over extended periods. This durability ensures a long service life and reduces the need for frequent replacement.
5. Versatility
As previously mentioned, molecular sieves find use in a wide range of applications across various industries. Their versatility makes them a valuable asset in many different processes, from petrochemical production to food preservation.
Key Benefits of Using Molecular Sieves in Various Industries
| Industry | Molecular Sieve Type | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Petrochemical | 5A | Efficient hydrocarbon separation, gas purification |
| Pharmaceutical | 3A, 4A | Solvent drying, API protection, moisture control in packaging |
| Food and Beverage | 3A, 13X | Moisture control, oxygen scavenging, extended shelf life |
| Air Separation and Compression | 13X, MSOX-500, MSOX-501 | High-purity oxygen generation, removal of impurities in compressed air |
Frequently Asked Questions on Molecular sieves types and applications
What is molecular sieve used for?
Molecular sieves are used for separating, purifying, and drying gases and liquids in a wide range of industries. Their ability to selectively adsorb specific molecules based on size and polarity makes them indispensable in:
Petrochemical industry: Purification and separation of gas streams, such as removing water, CO2, and sulfur compounds.
Natural gas processing: Drying gas and removing impurities.
Air separation: Producing pure nitrogen or oxygen in PSA (Pressure Swing Adsorption) systems.
Pharmaceuticals: Ensuring solvent purity and preventing moisture contamination in active ingredients.
Food preservation: Controlling moisture and oxygen levels in packaging to extend product shelf life.
What is meant by molecular sieving?
Molecular sieving refers to the selective adsorption of molecules based on their size and shape. Molecular sieves have uniformly sized pores that allow only molecules smaller than the pore size to pass through, while larger molecules are excluded. This allows for the effective separation and purification of components in a mixture, whether in gases, liquids, or solids. For example, 3A molecular sieves selectively adsorb water molecules while excluding larger molecules like hydrocarbons, making them ideal for drying applications.
What are 4A molecular sieves for?
4A molecular sieves are commonly used for gas and liquid drying, particularly in the removal of moisture, ammonia, and carbon dioxide from gas streams. Some key applications include:
Air separation and gas purification: Removing moisture to prevent freezing and corrosion in cryogenic systems.
Petrochemical processing: Removing water from feedstocks to protect catalytic processes.
Refrigeration systems: Preventing the formation of ice by removing moisture from refrigerants.
What is the difference between silica gel and molecular sieve?
Silica gel and molecular sieves are both desiccants used for drying and adsorbing moisture, but they differ in several key ways:
Silica gel: Made of amorphous silicon dioxide, silica gel has a broad pore size distribution and is commonly used for general moisture control. It is effective in low-humidity environments but has limited adsorption at higher temperatures.
Molecular sieve: Crystalline material (zeolites) with a uniform pore size, allowing for more selective adsorption. Molecular sieves can adsorb specific molecules such as water, CO2, and other polar compounds at a higher rate and under more extreme conditions than silica gel, making them more effective in industrial applications.
Are molecular sieves reusable?
Yes, molecular sieves can be regenerated and reused multiple times. Regeneration is achieved by heating the sieve to release the adsorbed molecules, restoring the sieve’s adsorption capacity. For example:
Heat regeneration: Applying heat (200-300°C) drives off adsorbed water or other molecules.
Vacuum regeneration: Lowering the pressure allows the molecular sieve to release the adsorbed gases.
After regeneration, the molecular sieve can be reused in its application, making it both cost-effective and environmentally friendly.
What are the advantages of molecular sieves?
Molecular sieves offer numerous advantages:
High adsorption capacity: Efficiently adsorb moisture, gases, and impurities.
Selectivity: The ability to selectively adsorb molecules based on size and shape, enhancing separation and purification efficiency.
Regenerability: Molecular sieves can be reused through regeneration.
Stability and durability: They operate well under extreme temperatures and pressures.
Versatility: They are used in various industries, including petrochemicals, natural gas, pharmaceuticals, and environmental applications.
How do molecular sieves remove water?
Molecular sieves remove water by adsorbing water molecules into their highly uniform microporous structure. The water molecules are drawn into the pores of the sieve, where they are trapped due to the strong electrostatic forces. This process effectively dries the surrounding gas or liquid, making molecular sieves ideal for applications like solvent drying, gas purification, and moisture control.
How much water can molecular sieves absorb?
The water adsorption capacity of molecular sieves varies depending on the type and operating conditions. Generally, molecular sieves can adsorb up to 20-30% of their weight in water. For instance, 3A molecular sieves are effective for high-efficiency drying, adsorbing up to 20% of their weight, making them suitable for applications where maximum water removal is needed.
What are molecular sieve 3A and 4A?
3A and 4A molecular sieves are both types of synthetic zeolites, each with a specific pore size that determines the size of molecules they can adsorb:
3A molecular sieve: Has a pore size of approximately 3 angstroms and is primarily used for drying gases and liquids by adsorbing water while excluding larger molecules like hydrocarbons.
4A molecular sieve: Has a slightly larger pore size of 4 angstroms and can adsorb molecules like water, ammonia, and carbon dioxide, making it more versatile in gas separation and purification processes.
What is a 3A molecular sieve used for?
3A molecular sieve is primarily used for drying and dehydrating gases and liquids, as its pore size is ideal for selectively adsorbing water molecules while excluding larger molecules like hydrocarbons. Applications include:
Drying gases: Hydrogen, oxygen, and natural gas.
Ethanol production: Dehydrating ethanol to achieve high purity.
Moisture control: In pharmaceutical, food, and petrochemical industries to prevent corrosion and product degradation.
What is type 5A molecular sieves?
5A molecular sieves have a pore size of approximately 5 angstroms and are used for gas and liquid separations. These sieves are particularly effective in:
Hydrocarbon separation: Separating normal paraffins from branched paraffins in petrochemical processes.
Natural gas purification: Removing moisture, CO2, and sulfur compounds from natural gas streams.
Oxygen and hydrogen purification: Used in PSA systems for generating high-purity oxygen and hydrogen.
How do I choose a molecular sieve?
To choose the right molecular sieve, consider the following:
Application: Whether you need drying, purification, or gas separation.
Molecular size: Select a sieve with a pore size that matches the molecule size you want to adsorb.
Desired purity: Determine the level of purity required for your gas or liquid.
Operating conditions: Consider temperature, pressure, and moisture content to select the right type of molecular sieve.
Can molecular sieves be used for CO2 removal?
Yes, molecular sieves like 13X are highly effective for carbon dioxide (CO2) removal from gas streams. They are commonly used in air separation, natural gas purification, and environmental applications such as carbon capture. The larger pore size of 13X sieves allows them to adsorb CO2 efficiently, helping reduce greenhouse gas emissions or purify gases for industrial uses.
How long do molecular sieves last?
The lifespan of a molecular sieve depends on the type of sieve, the environment it is used in, and the regeneration process. Generally, molecular sieves can last several years if properly regenerated and protected from contaminants like excessive water or oils. Periodic regeneration via heating or pressure changes restores their adsorption capacity, extending their lifespan.
What are molecular sieves made of?
Molecular sieves are typically made from zeolites, a crystalline aluminosilicate material with uniform, microporous structures. The most common types of molecular sieves include synthetic zeolites like 3A, 4A, 5A, and 13X, which differ in pore size and adsorption capacity depending on the ratio of silicon to aluminum in their structure.
Can molecular sieves adsorb other gases besides water?
Yes, molecular sieves can adsorb a wide variety of gases, depending on the pore size and the molecular properties of the gas. Besides water, molecular sieves are used to adsorb gases like:
CO2
Sulfur dioxide (SO2)
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S)
Ammonia (NH3)
Nitrogen (N2) This makes them versatile for gas separation and purification in various industrial applications.
What is the regeneration process for molecular sieves?
Molecular sieves are regenerated by removing the adsorbed molecules (like water or gases) to restore their adsorption capacity. This is typically done in two ways:
Thermal regeneration: Heating the molecular sieve to release the adsorbed molecules.
Pressure regeneration: Reducing the pressure in PSA (Pressure Swing Adsorption) systems, which forces the adsorbed gases to desorb from the sieve.
This process allows molecular sieves to be reused multiple times, making them cost-effective for continuous industrial applications.
Conclusion on Molecular sieves types and applications
Molecular sieves are indispensable tools in numerous industries due to their unique adsorption properties, selectivity, and versatility. By understanding the different molecular sieve types and their applications, businesses can optimize their processes, reduce costs, and improve overall product quality.
To wrap up this comprehensive exploration of molecular sieves and their various applications, it’s essential to highlight that these materials play a pivotal role across industries from petrochemicals to pharmaceuticals and environmental protection. For a deeper dive into how molecular sieves can be applied to your specific needs, be sure to check out our dedicated product hub on molecular sieves at Molecular Sieve, where you’ll find detailed information on different types of sieves and their industrial uses.
If you want to explore the mechanisms behind how molecular sieves function, take a look at our latest post: How Molecular Sieves Work. This article breaks down the science and practical applications of sieves in gas and liquid purification processes.
For those looking for an all-encompassing resource, don’t miss our cornerstone guide: Your Comprehensive Guide to Molecular Sieves 2024, where we offer a detailed overview of everything you need to know about molecular sieves, from their properties to specific industry case studies.
ทุกอย่างเกี่ยวกับ PSA Oxygen Concentration: คำถามที่พบบ่อย
